
An optical filter selectively transmits one portion of the optical spectrum, while rejecting other portions. Commonly used in microscopy, spectroscopy, chemical analysis, and machine vision,
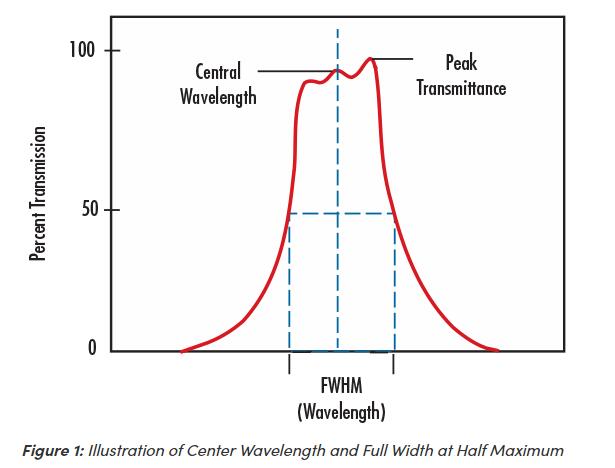
Central Wavelength
Center Wavelength (CWL), used in defining bandpass filters, describes the midpoint of spectral bandwidth over which the filter transmits. Traditional Coated Optical Filters tend to achieve a maximum transmission near the center wavelength, whereas Hard Coated Optical Filters tend to have a fairly flat transmission profile over the spectral bandwidth.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is a wavelength range used to denote a specific part of the spectrum that passes incident energy through a filter. Bandwidth is also referred to as FWHM (Figure 1).
Full Width-Half Maximum
Full Width-Half Maximum (FWHM) describes the spectral bandwidth over which a bandpass filter will transmit. The upper and lower limit of that bandwidth is defined at the wavelengths where the filter achieves 50% of the maximum transmission. For example, if the maximum transmission of the filter is 90%, the wavelengths at which the filter achieves 45% transmission will define the upper and lower limits of the FWHM. FWHM’s of 10nm or less are considered narrowband and often used for laser clean-up and chemical detection. FWHM’s of 25 – 50nm are often used in machine vision applications; FHWM’s of more than 50nm are considered broadband and typically used in fluorescence microscopy applications.
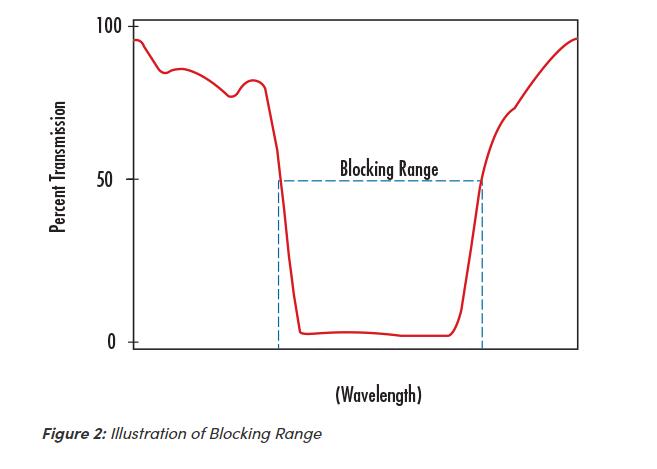
Blocking Range
Blocking Range is a wavelength interval used to denote a spectral region of energy that is attenuated by the filter (Figure 2). The degree of its blocking is typically specified in terms of optical density.
Slope
Slope is a specification often defined on edge filters, such as shortpass or longpass filters, to describe the bandwidth over which the filter transitions from high blocking to high transmission. Given as the percent of the cut-wavelength, slope can be specified from a variety of starting and end points. Herui Optics typically specifies the slope as the distance from the 10% transmission point to the 80% transmission point. For example, a 500nm longpass filter with a 1% slope would be expected to transition from 10% transmission to 80% transmission over a 5nm (1% of 500nm) bandwidth.
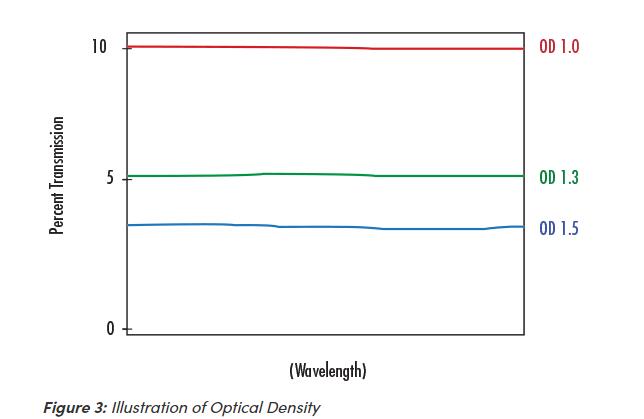
Optical Density
Optical Density (OD) describes the amount of energy blocked or rejected by a filter. A high optical density value indicates low transmission, and low optical density indicates high transmission. Optical densities of 6 or greater are used for extreme blocking needs such as Raman spectroscopy or fluorescence microscopy. Optical densities of 3.0 – 4.0 are ideal for laser separation and clean-up, machine vision, and chemical detection, while optical densities of 2.0 or less are ideal for color sorting and separating
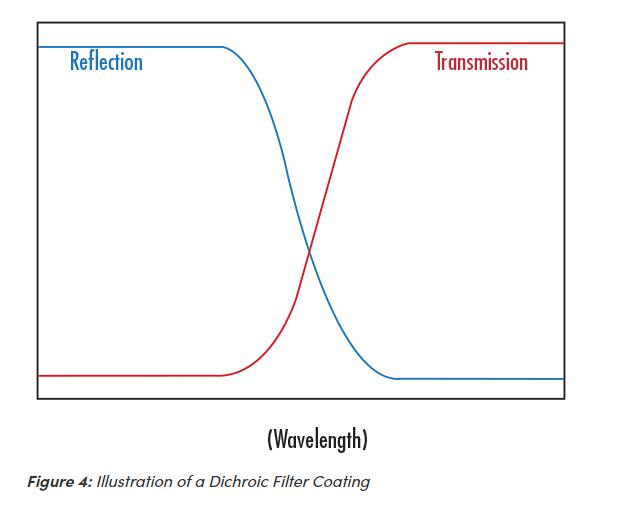
A Dichroic Filter is a type of filter used to transmit or reflect light, depending on the wavelength; light of a specific wavelength range is transmitted, while light of a different range is reflected or absorbed (Figure 4). Dichroic filters are commonly used for longpass and shortpass applications.
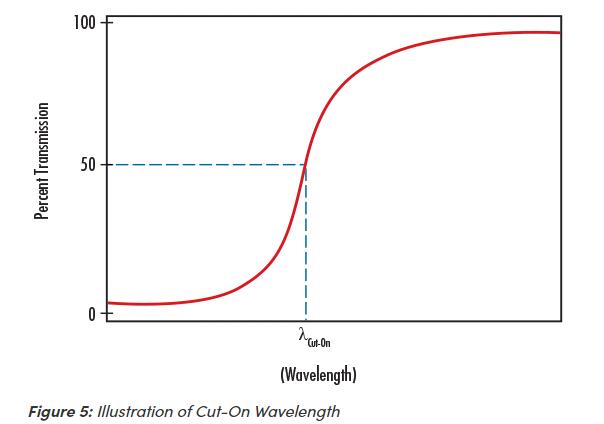
Cut-On Wavelength is a term used to denote the wavelength at which the transmission increases to 50% throughput in a longpass filter. Cut-on wavelength is indicated by λcut-on in Figure 5.
Cut-Off Wavelength
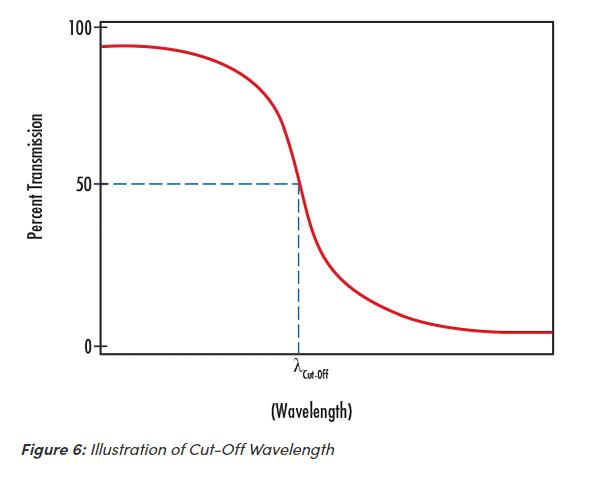
Cut-Off Wavelength is a term used to denote the wavelength at which the transmission decreases to 50% throughput in a shortpass filter. Cut-off wavelength is indicated by λcut-off in Figure 6.








 售前客服
售前客服