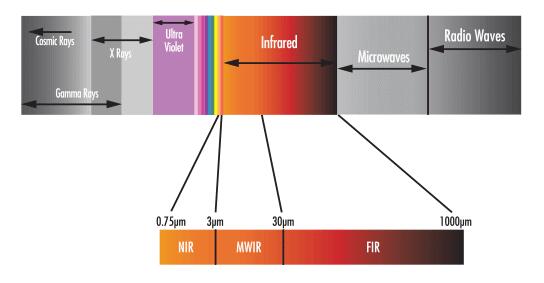
Infrared (IR) radiation is characterized by wavelengths ranging from 0.750 -1000μm (750 - 1000000nm). Due to limitations on detector range, IR radiation is often divided into three smaller regions: 0.750 - 3μm, 3 - 30μm, and 30 - 1000μm – defined as near-infrared (NIR), mid-wave infrared (MWIR), and far-infrared (FIR), respectively (Figure 1). Infrared products are used extensively in a variety of applications ranging from the detection of IR signals in thermal imaging to element identification in IR spectroscopy.
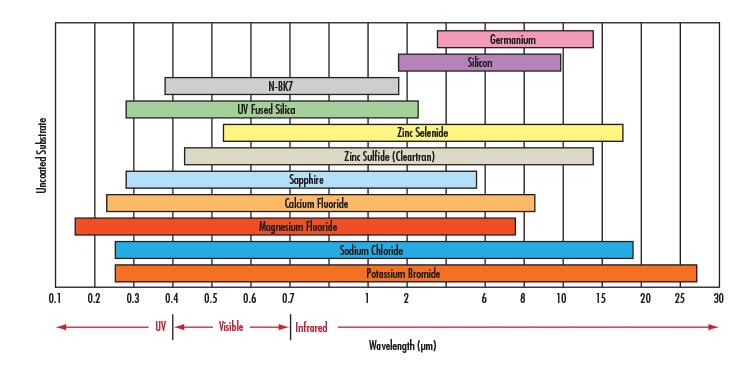
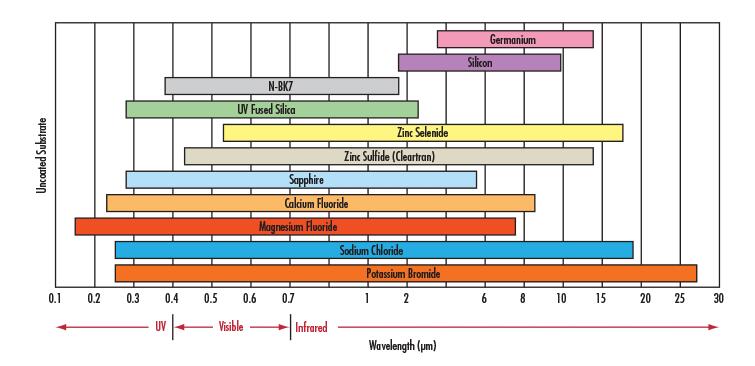
plano-optics (i.e. windows, mirrors, polarizers, beamsplitters, prisms), spherical lenses (i.e. plano-concave/convex, double-concave/convex, meniscus), aspheric lenses (parabolic, hyperbolic, hybrid), achromatic lenses, and assemblies (i.e. imaging lenses, laser beam expanders, eyepieces, objectives). These IR materials, or substrates, vary in their physical characteristics. As a result, knowing the benefits of each allows one to select the correct material for any IR application.








 售前客服
售前客服